Knowing how to choose long term stocks and investing in the right stocks for the long term is never easy. There are many options that you can go for. You can search from billions of individual stocks, ETFs, bonds, commodities, and many other options. Yet, stocks stay as one of the most favorable investment assets of our time. It is not only easy to invest in, but they also provide many benefits like high liquidity, higher returns, and cash-flow.
No matter how easy it is, many investors struggle to understand the financial markets. They can’t tell which stocks are solid long-term investments and which aren’t which makes it harder to choose long term stocks. To invest for the long run, you must not only consider specific indications. You must also focus on your long-term aims, have discipline, and understand your long-term objectives. In this article, we will talk about stock picking strategies, what you should focus on, and the important details to be aware of.
Know Your Goals to Choose Long Term Stocks
The most important thing when doing anything is to know why you are doing it. You have to have a purpose. When it comes to knowing how to choose long term stocks, there are many things that you can consider. The answer to question how to choose long term stocks to buy for long-term investment lies in knowing your goals.
How to choose long term stocks, especially good long term stocks, depends on your goals and those goals has to be clear for you. If you want cashflow, you look for dividend stocks, if you want capital gains and earn more money on average, you look for growth stocks. If you like boring and safe stocks, you look at decade-old companies doing well both in business and in the stock market.
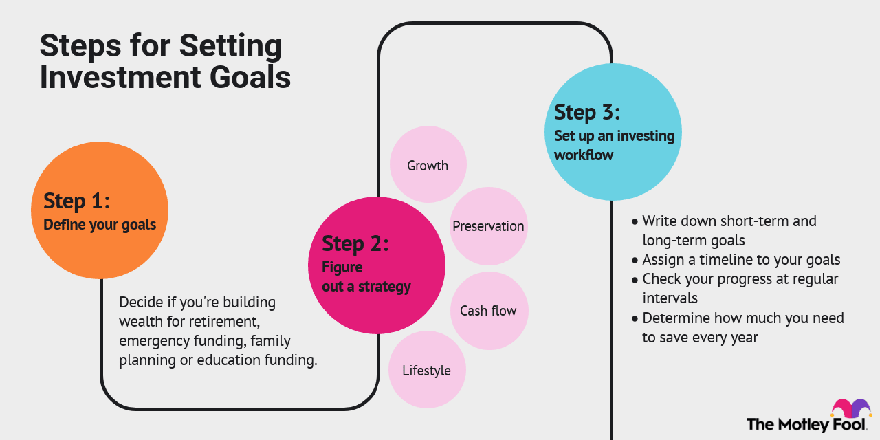
At this point, your research point must be within the area that you have an interest in. For example, if you like income, you oould focus on dividend stocks like Apple, Microsoft, Abbvie, etc.
But, if you like capital gains and want to buy and sell you need to focus on short-term. If that is the case, you must buy companies that you believe will rise in the short-term. That is how the process of how to pick good stocks goes in the first phase. I will explain two most used ways of stock investing below.
Dividend Stocks
Dividend stocks, if you are interested in the finance and stock area, are very popular among investors. They give you good gains and a cashflow in the long-term. However, one drawback (for many people) of dividend investing is the low amount of income you get versus the capital you have.
On average, dividend portfolios and stocks average a 3.5% return with their yields annually (just the money you get as dividends). Compared to real estate, bonds, or commodities this could be average or even higher than these. People still regard it as low but in fact, it is not.
The biggest factor here is that you get a steady flow of income and your capital also increases. With dividend stocks, your time horizon to hold the stocks are for the long-term. Generally, the ideal horizon is minimum of 10 to 15 years. Nevertheless, many people buy these stocks to never sell and keep buying them. This increases the cash flow to be able ty live with them.
Unlike other investment strategies like just holding onto the asset until they appreciate enough in capital to give you enough to live-by with, dividend strategy is only for cashflow. There are some people on the internet who does well explaining the comprehensive method on finding good dividend stocks.
Growth Stocks
Growth stock strategies are extremely different than dividend investing. This strategy focuses on capital increases, generally by overperforming the entire stock market. They are higher risk but higher reward. Biggest examples to growth stocks today are stocks like Palantir, DataDog, and Zoom.
However, they have lost more than %70 of their value YTD (as of 16th March) but they gained more than %200 over the last 5 years. These stocks can both be for trading or long-term holding if you trust the company enough.
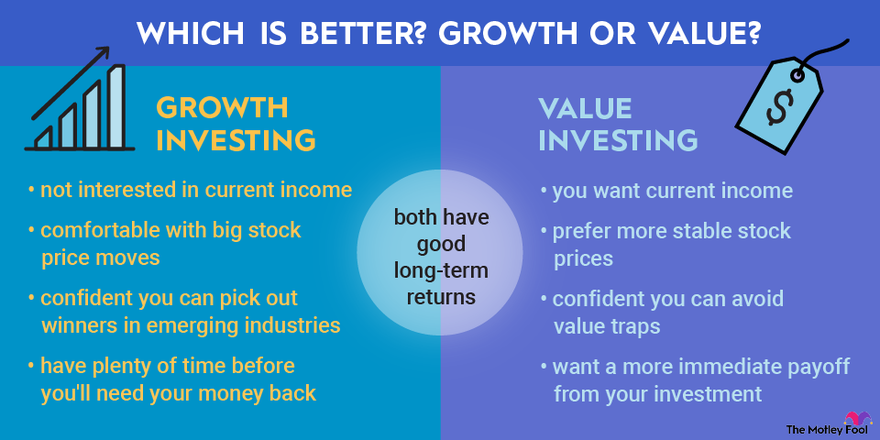
Putting money in growth stocks is not something that everyone chooses to do. The reason for that is because the risk involved is high for many people. However, the time horizon is way shorter than dividend stocks. You could also use growth stocks for day-trading to get short-term value to your capital.
Fundamentals of How to Choose Long Term Stocks
Analysts examine a variety of basic variables to determine which companies are suitable long-term investments and which are not. These criteria show if the firm is financially strong and whether the stock price has been reduced to below its true worth, making it a suitable investment.
The tactics listed below might help you assess the value of a stock. However, please keep in mind that economic fundamentals of a company might not determine its future all the time. Other things such as management and long-term plans are also a good indicator.
Consistency
The constancy with which a company’s capacity to pay and enhance its dividend demonstrates that its earnings are predictable. It also demonstrates that it is financially secure enough to pay the dividend (from current or retained earnings). There are many various viewpoints on how many years you should go back to find this consistency—some say five years, some say up to 20—but anyplace in this range will give you an indication of dividend constancy.
P/E or Other Ratios
The price/earnings ratio (P/E) is a popular technique for determining whether a business is overpriced or undervalued. Yout determine this ratio by dividing the current stock price by the earnings per share of the firm. The greater the P/E ratio, the more the willingness of certain investors to pay for such earnings. A greater P/E ratio, on the other hand, is considered as an indication that the stock is expensive and may be ready for a drop. A lower P/E ratio may signal that the company is a good buy and that markets have driven shares below their true worth.

There are also other ratios like price to book value or price to book, etc. Each of these ratios signal a different value that you must take a look at. Depending on the type of the company and the fundamental you want to understand, calculate or research that ratio. For example, with REITs, P/E ratios are generally higher than normal because they work on a different business model.
Earning Reports
The economy goes through cycles. When the economy is healthy, incomes grow. At other times, the economy slows and wages plummet. One approach to tell if a stock is a solid long-term investment is to look at its previous earnings and future earnings estimates. If the firm has a lengthy history of increasing earnings, it might be an excellent long-term investment.
Is it a Value Trap?
How can you tell if a stock is a solid long-term investment and not a value trap (a stock that appears inexpensive but has the potential to fall far lower)? To answer this issue, employ basic common sense concepts, such as examining the company’s debt and current ratios.
The debt ratio calculates the amount of debt used to fund assets. You can calculate this ratio by dividing the overall liabilities of the firm by the total assets. In general, the more the debt, the greater the likelihood that the firm would be a value trap.
How to Identify Value Traps When Choosing Long Term Stocks
Value traps can be difficult to spot. A thorough fundamental research of the stock can help you distinguish between them and solid investment opportunities. The value trap can trap investors looking for deals in the stock market. A stock that is trading at a low PE ratio or at a declining price may end up being a trap rather than a good investment.
Falling Sales
It indicates declining market share. When new, more effective competitors enter the market, it will affect the sales of a company. These kind of new enterprises will force bad companeis to go out of business. New businesses will take their place.

It is worth remembering that you should not draw conclusions from a few years’ worth of data. Ten to fifteen years’ worth of data must be available to check. Additionally, yoı must consider operating revenue rather than overall income. That is because due to the fact that you should prefer to omit the contributions of outside revenue. A corporation is a value trap if it has recorded a sustained decline in “revenue from operating” figures.
Its EPS is at Its Peak
Value investors must stay away from stocks with with EPS. This generally happens for cyclical stocks. Cyclical companies’ earnings fluctuate between highs and lows. These businesses exhibit significant EPS fluctuations over the course of a few years. Their PE ratio decreases when EPS is high. Investors are more prone to purchase their stocks by this.
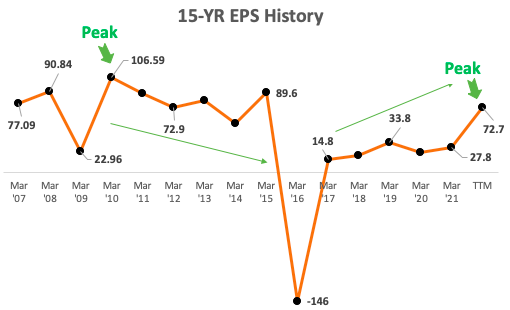
When cyclical stocks reach their high, their EPS starts to decline. This is when the price of the stock begins to decline along with the demand for such equities. When no one is purchasing cyclical stocks, that is the ideal time to acquire them. This stage could last for three to four years. Investors must be patient and be ready to hold it for long-term. One method to avoid falling into the value trap is to avoid buying cyclical firms at their highest EPS levels.
Interest Coverage Ratio
We have witnessed some well-known brand names disintegrate in the past. Bankruptcy is one of the factors that led to their demise. Companies choose bankruptcy when they are no longer able to repay their loans. Such businesses are a foregone conclusion to be a value trap. How do you recognize them? based on their ICR trend. It measures the proportion of interest to EBIT for the business.
A warning sign is the declining ICR and rising debt to equity ratio (D/E).




