In investing, learning how to create a diversified portfolio is often seen as one of the most important parts of personal finance journey. Learning how to create a diversified portfolio will give you access to higher returns and it is one of the most effective strategies for long-term success. But how to create a diversified portfolio and what exactly does it mean to have a diversified portfolio?
A diversified portfolio refers to spreading your investments to more than one asset, like investing in stocks, bonds, real estate, and commodities altogether. So, when you are learning how to create a diversified portfolio, you learn how to diversify your money across different assets. The goal of asset portfolio diversification is to reduce the overall risk by not putting all your eggs in one basket. With diversification, you can minimize the impact of a single investment’s performance on your overall portfolio.
In this post, we will talk about the basics of portfolio diversification and provide a step-by-step guide on creating a diversified portfolio that matches your investment goals for the future and risk tolerance.
Understanding the Basics of Portfolio Diversification
The first step to learning how to create a diversified portfolio is understanding the portfolio diversification. Portfolio diversification is a very old and important strategy in investment strategy. It involves spreading your portfolio to different asset classes like stocks and bonds to reduce the risk and increase returns.

Why is Diversification Important?
Learning how to create a diversified portfolio is important for several reasons. If you understand these reasons, you can diversify your portfolio better and more easily.
- Risk Reduction. Diversifying your investments helps reduce the impact of market volatility and potential losses. If one investment underperforms, the positive performance of other investments can cushion the overall impact on your portfolio.
- Potential for Higher Returns. By having a mix of asset classes in your portfolio, you can benefit from these assets’ varying performance over time. This can lead to a more balanced and potentially higher overall return.
- Preservation of Capital. Diversification helps preserve capital by avoiding overexposure to any asset or sector. By spreading your investments, you reduce the risk of significant losses if a particular investment performs poorly.
Core Principles of Portfolio Diversification
You can learn to create a diversified portfolio in very different ways. A combination of almost all of the types of diversification will generally yield the best results and the lowest changes in your total portfolio’s value. Here are the core principles and types of diversification that you can learn to create a diversified portfolio.
- Asset Class Diversification. You can diversify your investments by choosing to invest across asset classes. These asset classes could be stocks, bonds, real estate, commodities, and cash. Each asset class has its own return and loss risk, and they tend to perform differently under various market conditions.
- Geographic Diversification. Investing in different geographical areas can help reduce risk by spreading your exposure across different economies and markets. This can protect your portfolio from being overly influenced by the performance of a single region.
- Sector Diversification. Consider diversifying your investments across different sectors or industries within each asset class. This helps reduce the impact of any specific sector’s performance on your portfolio.
- Company Size Diversification. Diversify your investments across companies of different sizes, such as large-cap, mid-cap, and small-cap stocks. Different-sized companies may perform differently based on market conditions, and spreading your investments across these categories can help balance risk.
- Time Diversification. Invest over different time periods rather than trying to time the market. Diversification of time horizons helps smooth out the impact of market fluctuations on short and mid-term movements and reduces the risk of losing money due to poor investment decisions.
Understanding Correlations and Covariances
When diversifying your portfolio, it is essential to understand the concepts of correlations and covariances between different assets. Correlation is essentially the relationship between the price movements of two assets. A correlation coefficient of +1 says that there is a perfect positive correlation, while a coefficient of -1 indicates a perfect negative correlation. A coefficient of 0 indicates no correlation.
Covariance measures the extent to which two assets move together. A positive covariance means the assets move in the same direction, while a negative covariance indicates they move in opposite directions.
By understanding correlations and covariances, you can choose to invest in assets that have low or negative correlations with each other. This helps to further diversify your portfolio and reduce the risk of all your investments moving in the same direction.
In summary, understanding the basics of portfolio diversification is crucial for building a strong investment strategy. By diversifying across asset classes, geographic regions, sectors, company sizes, and time periods, you can reduce risk and potentially enhance returns. Additionally, understanding correlations and covariances enables you to select assets that complement each other and further diversify your portfolio.
Identifying Your Investment Goals and Risk Tolerance
It doesn’t matter what kind of diversification you are doing; if you don’t know your investment goals and risk tolerance, you will not make good decisions. Understanding your objectives and the level of risk you are willing to take on will help you shape your investments and help you build a portfolio that matches your financial aspirations.
Why Identifying Goals and Risk Tolerance is Crucial
- Clarity of Purpose. Clearly defining your investment goals helps you stay focused and committed to your financial objectives. Whether your goals include saving for retirement, funding your children’s education, or purchasing a home, having a clear understanding of what you want to achieve will guide your investment strategy.
- Risk Management. Identifying your risk tolerance is essential in managing the level of risk you are comfortable with. Certain investors have a higher risk tolerance and can tolerate higher volatility and potential losses for the possibility of making higher returns. Some individuals prefer a conservative approach by prioritizing capital over aggressive growth. Knowing your risk tolerance will guide your asset allocation decisions and help you find a balance between risk and reward.
How to Set Investment Goals
- Define Your Short-Term and Long-Term Goals.
Determine your financial objectives and categorize them as short-term (within the next few years) or long-term (10 years or more). Short-term goals may be a vacation that you want or a down payment on a mortgage for a house. Long-term goals could be retirement planning or building a substantial investment portfolio.
- Quantify Your Goals.
Assign specific dollar amounts or percentages to your goals. This will provide clarity and help you determine how much you need to invest to achieve your objectives.
- Prioritize Your Goals.
Order your goals based on importance and urgency. This will help you allocate your resources and focus on the goals that matter most to you.
- Consider Time Horizon.
Consider the time you have until you need the funds for each goal. You can have a more aggressive investment approach with longer-term investments, while shorter-term goals may require a more conservative investment strategy.

Determining Your Risk Tolerance
- Evaluate Your Financial Situation. Take a good look at your current financial position. Calculate your income, expenses, assets, and liabilities. Understanding your financial stability and capacity to handle risk is essential in determining your risk tolerance.
- Assess Your Investment Knowledge and Experience. Consider your level of investment knowledge and experience. If you are a novice investor, you may have a lower risk tolerance initially until you gain confidence and experience in the market.
- Consider Your Emotional Comfort with Risk. Reflect on how comfortable you are with the possibility of losing money in your investments. Some individuals are more risk-averse and prefer to avoid significant fluctuations, while others are more resilient and can tolerate higher levels of volatility.
- Consult with a Financial Advisor. Work with a financial advisor to help you assess your risk tolerance. They can help you evaluate your financial situation, understand your goals, and determine an appropriate level of risk for your investment portfolio.
Choosing the Right Mix of Assets
Choosing the right mix of assets is a critical step in creating a diversified portfolio. It involves selecting a combination of different assets that match your goals and risk tolerance. You can reduce the overexposure to an investment and potentially enhance your portfolio’s overall performance by diversifying across asset classes.
Understanding Different Asset Classes
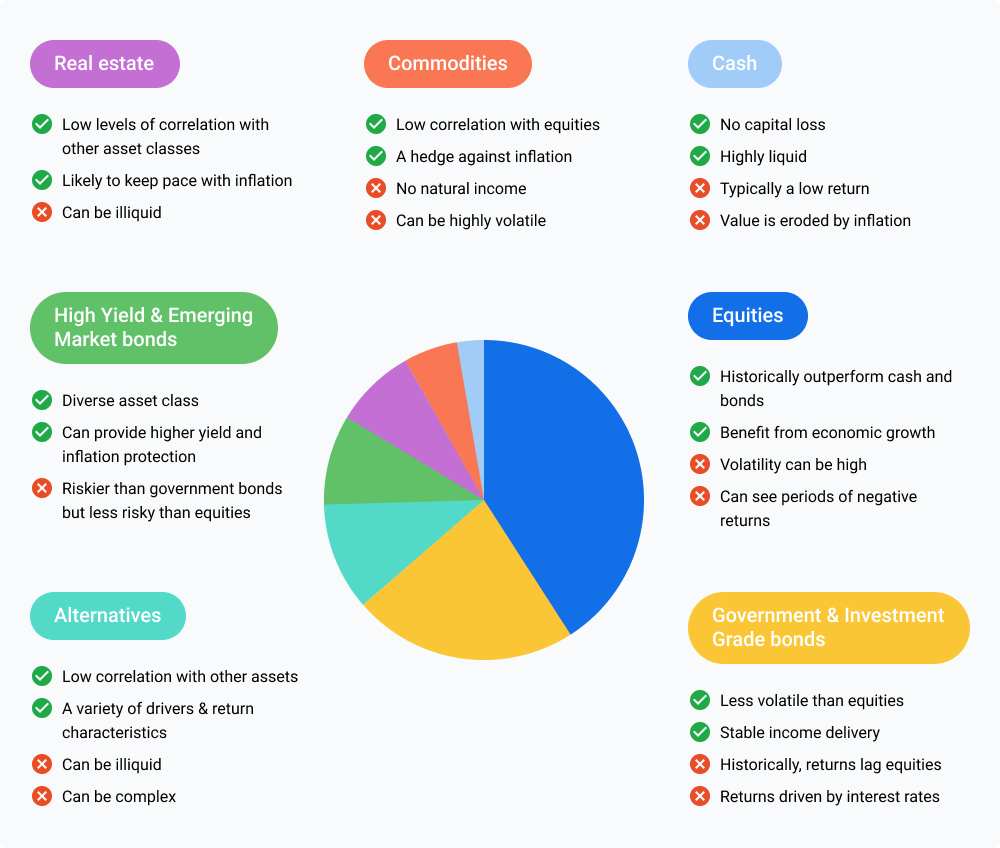
- Stocks. Stocks means having ownership in a company through them. They offer capital appreciation and dividend potential depending on the stock. They are often considered higher-risk, higher-reward investments and can provide long-term growth opportunities.
- Bonds. Bonds are debt securities that are generally issued by governments, municipalities, or corporations. The bonds offer fixed interest payments over a specified period and are generally considered lower-risk investments compared to stocks. Bonds provide income and can help preserve capital.
- Real Estate. Real estate investments involve purchasing properties, such as residential, commercial, or industrial buildings. Real estate can provide income through rental payments and potential capital appreciation over time. It is considered a tangible and relatively stable asset.
- Commodities. Commodities are literally physical goods such as gold, oil, natural gas, agricultural products, and more. Investing in commodities generally gives you a good hedge against inflation and diversification benefits, as their performance is often independent of traditional financial markets.
- Cash and Cash Equivalents. Cash and cash equivalents are things like savings accounts, money market funds, and short-term government or other type of bonds. They are hot cash or quickly available cash that provides stability and liquidity. They serve as a haven and can be used for emergencies or short-term investment needs.
How to Allocate Assets Based on Goals and Risk Tolerance
Now, you know about your investment goals, risk tolerance, and what you are willing to invest in based on these two things. The next step is to determine the allocation of assets based on these specific goals and the tolerance you have. You must choose the right allocation to keep your diversification stable.

Determine your Asset Allocation Strategy
Asset allocation is the distribution of your investments across different asset classes. It is based on your investment goals, risk tolerance, and time horizon. Common approaches to asset allocation include aggressive, moderate, and conservative portfolios.
Consider Time Horizon
Longer-term goals typically allow for a higher allocation to growth-oriented assets like stocks, while shorter-term goals may require a more conservative allocation with a higher focus on income-generating assets like bonds.
Evaluate Risk Tolerance
Assess your risk tolerance and allocate assets accordingly. If you have a higher risk tolerance, you may have a higher allocation to stocks, whereas a lower risk tolerance may lead to a higher allocation in bonds and cash equivalents.
Diversify Within Asset Classes
Within each asset class, further diversify your investments. For example, within stocks, consider investing in different industries, sectors, or geographical regions to reduce concentration risk.
Rebalance Periodically
Frequently review and rebalance your portfolio, preferably on a schedule, to maintain your desired asset allocation. Over time, certain asset classes may outperform or underperform, leading to a deviation from your original allocation. Rebalancing makes sure that your portfolio is always aligned with your investment strategy.
Importance of Rebalancing Your Portfolio
When certain investments outperform others, it can lead to an imbalance in your asset allocation. Rebalancing means you basically sell investments that have exceeded their target allocation and reallocate the funds to underrepresented assets. This process helps maintain the intended risk and return characteristics of your portfolio.
Regularly rebalancing your portfolio ensures that you are not overly exposed to a single asset class and allows you to take advantage of market opportunities. It also helps manage risk by preventing your portfolio from becoming too heavily weighted towards a specific investment.
Investing in Different Geographical Areas
Investing in different geographical areas is an important aspect of portfolio diversification. By spreading your investments across various regions, you can get the potential growth and stability of different economies.
Different geographical areas could give you different economic growth opportunities. You access a broader range of economic levels of growth by investing in different countries and continents. Different countries and regions may have different levels of economic expansion, providing the potential for higher returns compared to investing solely in your local market.
International diversification can also give you exposure to sectors and industries that may not be prominent in your home country. This allows you to take advantage of emerging industries and potentially benefit from their growth.
You can also get away from inflation in your own currency, which will provide currency diversification benefits. Holding investments denominated in different currencies can help protect you from the impact of exchange rate fluctuations on your portfolio.
Lastly, spreading your investments across different geographical areas can reduce the overexposure risk to the performance of a single country or region. Political, economic, or market-specific risks that may impact one country or region may not necessarily affect others in the same way.
Pros of International Investing
- Better range of economic growth opportunities,
- More industries and sectors to invest in,
- Less currency inflation effect,
- Less exposure to one geographical risk like political, economic, or market-specific risks.
Cons of International Investing
- The currency might plunge, leaving you with a currency risk.
- You might not have a complete overview of the policies and regulations that will come into effect,
- Overall economic and market risks,
- Less information and transparency.
How to Choose Foreign Investments
- Research and Analysis. Conduct thorough research on the economies, political stability, and regulatory environments of the countries you are considering for investment. Assess the growth potential, market conditions, and risks associated with specific regions.
- Diversify Across Countries. Select investments across different countries to diversify your exposure. Consider investing in developed markets, emerging markets, and frontier markets to achieve a balanced geographic diversification.
- Understand Cultural and Market Differences. Study the cultural nuances and market dynamics of the countries you are considering very well and understand them. Factors such as business practices, consumer behavior, and cultural norms can impact the success of investments.
- Seek Professional Advice. If you are unfamiliar with international investing or lack the necessary expertise, consider getting help from a financial advisor or an experienced investment professional who specializes in global markets. They can provide insights and help you navigate the complexities of international investing.
Maintaining and Reviewing Your Diversified Portfolio
Maintaining and reviewing your diversified portfolio is essential to ensure its continued alignment with your investment goals and risk tolerance. Regular monitoring, periodic reviews, and necessary adjustments are crucial to maximize the effectiveness of your portfolio and respond to changing market conditions.
Regular Review of Your Portfolio
- Set a Review Schedule. Establish a regular schedule to review your portfolio. The frequency of reviews may vary depending on your investment strategy and market conditions, but a general guideline is to conduct a comprehensive review at least annually.
- Assess Performance. Evaluate the performance of your investments against their respective benchmarks and your overall portfolio objectives. Identify investments that are underperforming or overperforming and determine the reasons behind their performance.
- Monitor Asset Allocation. Always make sure and follow that your asset allocation is in line with your desired strategy. Revisit your target allocation and compare it to the current allocation of your portfolio. If there are significant deviations, consider rebalancing to bring it back to the desired levels.
- Evaluate Risk Exposure. Assess the level of risk in your portfolio and see if it aligns with your risk tolerance. Consider the impact of any changes in your financial situation or risk appetite and adjust your portfolio accordingly.
How to Adjust Your Portfolio When Necessary
- Rebalance Your Portfolio. If your portfolio has deviated significantly from your target asset allocation, consider rebalancing. Sell investments that have exceeded their target allocation and reallocate the funds to underrepresented asset classes. This ensures that your portfolio remains diversified and aligned with your investment strategy.
- Review Individual Investments. Assess the performance and outlook of individual investments in your portfolio. If an investment no longer meets your criteria or if its fundamentals have changed, consider selling it and reinvesting in a more suitable opportunity.
- Tax Efficiency. Consider the tax implications of any portfolio adjustments. Selling investments may trigger capital gains taxes, so it is important to evaluate the potential tax consequences and consult with a tax advisor if needed.
- Stay Informed. Stay updated with relevant news, market trends, and economic indicators that may impact your investments. This information can help you make informed decisions about adjusting your portfolio.
Conclusion
Learning how to create a diversified investment portfolio is a smart move for long-term success. It’s all about spreading your investments across different types of assets to reduce risk. Understanding why diversification matters is key. It helps cushion the impact of market ups and downs, potentially leading to more balanced returns and safeguarding your money from heavy losses in any single investment.
The core idea? Spread your investments! Think stocks, bonds, real estate, commodities, and cash. Mix it up based on your goals and how much risk you’re comfortable with. Knowing your goals and risk tolerance upfront guides your decisions. Are you aiming for long-term growth or safeguarding what you have? Understanding this helps shape your investment strategy.
And don’t forget about global investments. Diversifying across different countries and regions gives you exposure to various markets and economic situations, reducing your reliance on a single area’s performance.
Lastly, keep an eye on your investments. Regular check-ins and adjustments ensure your portfolio stays in line with your goals and changing market conditions. By diversifying smartly, you’re setting yourself up for a more secure and potentially rewarding investment journey.
Top of Form